“Unfortunately, experiencing a cyber incident is common for Australian SMBs. Of those surveyed, 62% had experienced a cyber incident.”
Australian Cyber Security Centre – Small Business Survey
Artificial Intelligence is transforming every aspect of our lives – including the threat landscape. For managed service providers supporting small businesses, the rise of AI-driven cyber threats is both a challenge and an opportunity. While AI offers powerful new tools for defence, it is equally enabling cybercriminals to launch more sophisticated, scalable and convincing attacks. The implications for SMBs – often with limited in-house security resources – are significant.
How AI Is Empowering Cybercriminals
Traditionally, cyber attacks required an investment of time and technical skill, especially targeted spearphishing campaigns. Today, AI lowers the barrier to entry for threat actors, enabling them to craft highly convincing, large-scale attacks with unprecedented speed and accuracy.
1. Scalable Attacks Across Smaller Targets
SMBs were once thought to have “security by obscurity”: too small to attract attention from cybercriminals. That’s no longer true. AI allows bad actors to automate reconnaissance and target thousands of smaller organisations simultaneously. This shift has turned SMBs into low-hanging fruit, and MSPs are now on the frontlines of protecting these vulnerable clients.
AI can crawl websites, business directories and social media platforms to gather information about a company’s structure, personnel and operations. This data is then used to tailor phishing emails that bypass generic spam filters and resonate with recipients. SMBs, without robust security frameworks or dedicated cyber teams, are particularly susceptible to such tailored attacks.
2. Hyper-Personalised Messaging
Using natural language processing and machine learning, attackers can craft emails that mimic the tone, structure, and even the quirks of a specific sender’s writing style. A message that appears to come from the CEO to the finance department requesting an urgent payment can now sound eerily authentic, increasing the chances of success.
True Story
For MSPs, this raises the stakes. Traditional email filtering and basic security awareness training may no longer be enough. Solutions must now include behavioural analytics and real-time threat detection capable of identifying anomalies in communication patterns.
3. Improved Language, Fewer Errors
One of the past giveaways of a phishing attempt was poor grammar, awkward phrasing, or obvious spelling errors. AI-powered writing tools, however, can generate content that reads naturally and is virtually indistinguishable from legitimate business communication. These grammatically correct and professional-looking messages reduce the red flags users might otherwise notice. This development calls for a renewed focus on advanced email security tools that analyse more than just content; they need to evaluate metadata, context, sender history, and timing to flag suspicious messages.
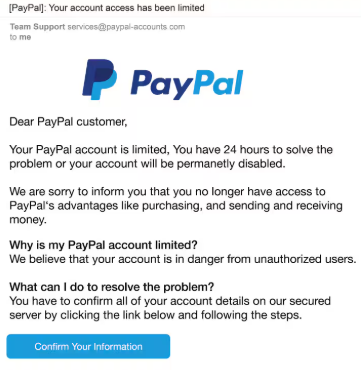
4. Multi-Source Data Integration for Plausibility
Modern spearphishing doesn’t rely on guesswork. AI can synthesise data from various sources: public records, social media activity, press releases, even company newsletters, to create emails that are believable and timely. For example, an email referencing a recent company announcement or a specific employee’s promotion might seem perfectly plausible to the recipient.
This level of verisimilitude makes it harder for users to distinguish between legitimate and malicious emails, increasing the likelihood of a successful breach.
What We Can Do
“80% of SMBs surveyed said cybersecurity was “important” or “very important”, yet almost half reported spending less than $500 a year on it.”
Australian Cyber Security Centre – Small Business Survey
For MSPs, the challenge is to be proactive and stay one step ahead:
- Fight Fire with Fire: Just as AI is being used to launch attacks, it can also be used to defend against them. Tools like Avanan and Guardz that use machine learning to detect anomalies, behavioural shifts, or suspicious access patterns are essential.
- Ongoing Education: Security awareness training must evolve. Simulated phishing attacks, training on recognising AI-enhanced threats, and fostering a culture of security mindfulness are crucial.
- Layered Security Approaches: No single solution is foolproof. A multi-layered approach incorporating endpoint protection, identity and access management, email filtering, and backup systems provides the strongest defence.
- Partner With Cloud-Native Security Solutions: Providers like Avanan, which integrate directly into cloud platforms and scan for threats both before and after native security layers, offer advanced protection that’s essential in today’s AI-augmented threat environment.
AI has fundamentally altered the cybersecurity landscape, especially for SMBs who may not have the internal expertise to combat these evolving threats. For MSPs in Australia and New Zealand, this is an opportunity to provide guidance, demonstrate value and convince reluctant clients to invest in security. By embracing AI-powered defences and educating clients about the risks, MSPs can turn today’s challenges into tomorrow’s strategic advantages.
DID YOU KNOW: Using AI for business productivity comes with its own share of risks. This paper from the Australian Signals Directorate provides details and recommended actions.







